Data Products
🤝 Version compatibility
Open Source DataHub: 0.10.3 | Acryl: 0.2.8
What are Data Products?
Data Products are an innovative way to organize and manage your Data Assets, such as Tables, Topics, Views, Pipelines, Charts, Dashboards, etc., within DataHub. These Data Products belong to a specific Domain and can be easily accessed by various teams or stakeholders within your organization.
Why Data Products?
A key concept in data mesh architecture, Data Products are independent units of data managed by a specific domain team. They are responsible for defining, publishing, and maintaining their data assets while ensuring high-quality data that meets the needs of its consumers.
Benefits of Data Products
Data Products help in curating a coherent set of logical entities, simplifying data discovery and governance. By grouping related Data Assets into a Data Product, it allows stakeholders to discover and understand available data easily, supporting data governance efforts by managing and controlling access to Data Products.
How Can You Use Data Products?
Data Products can be easily published to the DataHub catalog, allowing other teams to discover and consume them. By doing this, data teams can streamline the process of sharing data, making data-driven decisions faster and more efficient.
Data Products Setup, Prerequisites, and Permissions
What you need to create and add data products:
- Manage Data Product metadata privilege for Domains to create/delete Data Products at the entity level. If a user has this privilege for a given Domain, they will be able to create and delete Data Products underneath it.
- Edit Data Product metadata privilege to add or remove the Data Product for a given entity.
You can create this privileges by creating a new Metadata Policy.
Using Data Products
Data Products can be created using the UI or via a YAML file that is managed using software engineering (GitOps) practices.
Creating a Data Product (UI)
To create a Data Product, first navigate to the Domain that will contain this Data Product.
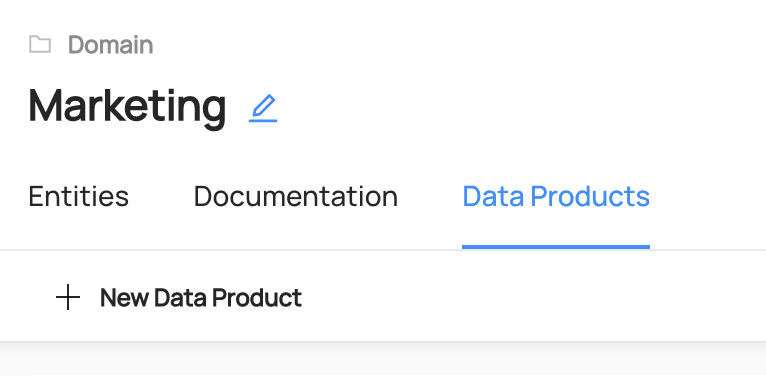
Then navigate to the Data Products tab on the Domain's home page, and click '+ New Data Product'. This will open a new modal where you can configure the settings for your data product. Inside the form, you can choose a name for your Data Product. Most often, this will align with the logical purpose of the Data Product, for example 'Customer Orders' or 'Revenue Attribution'. You can also add documentation for your product to help other users easily discover it. Don't worry, this can be changed later.
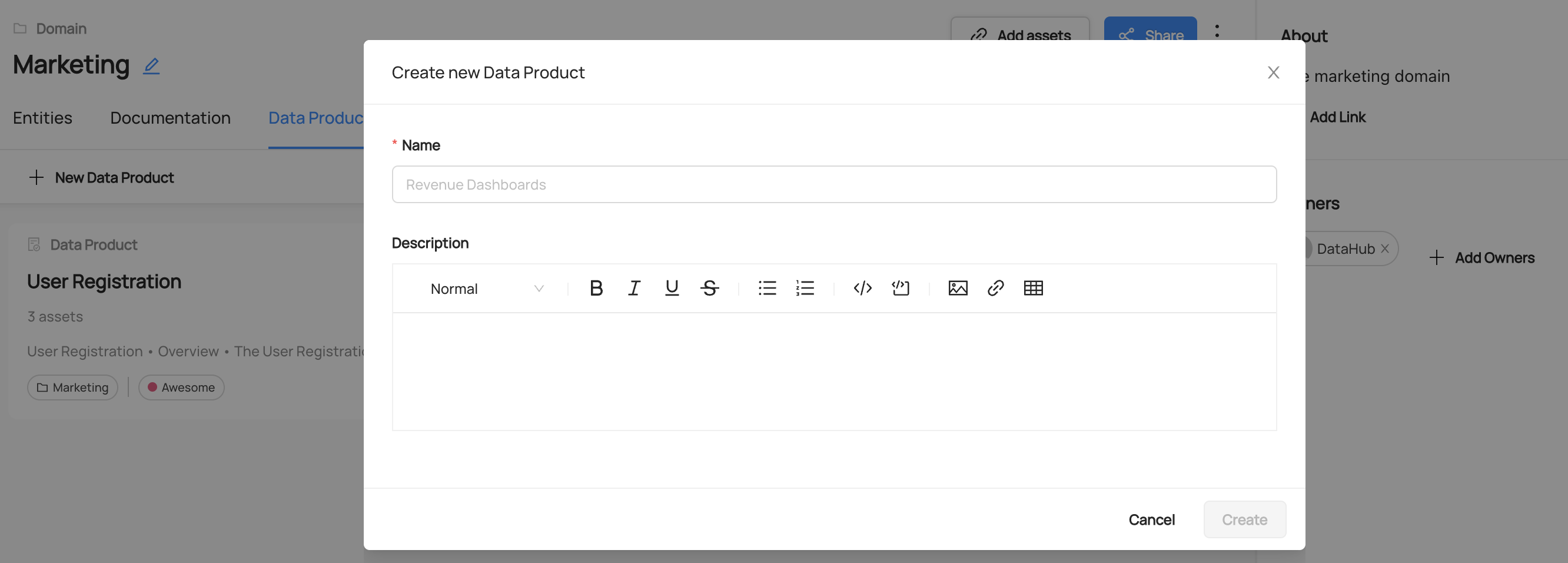
Once you've chosen a name and a description, click 'Create' to create the new Data Product. Once you've created the Data Product, you can click on it to continue on to the next step, adding assets to it.
Assigning an Asset to a Data Product (UI)
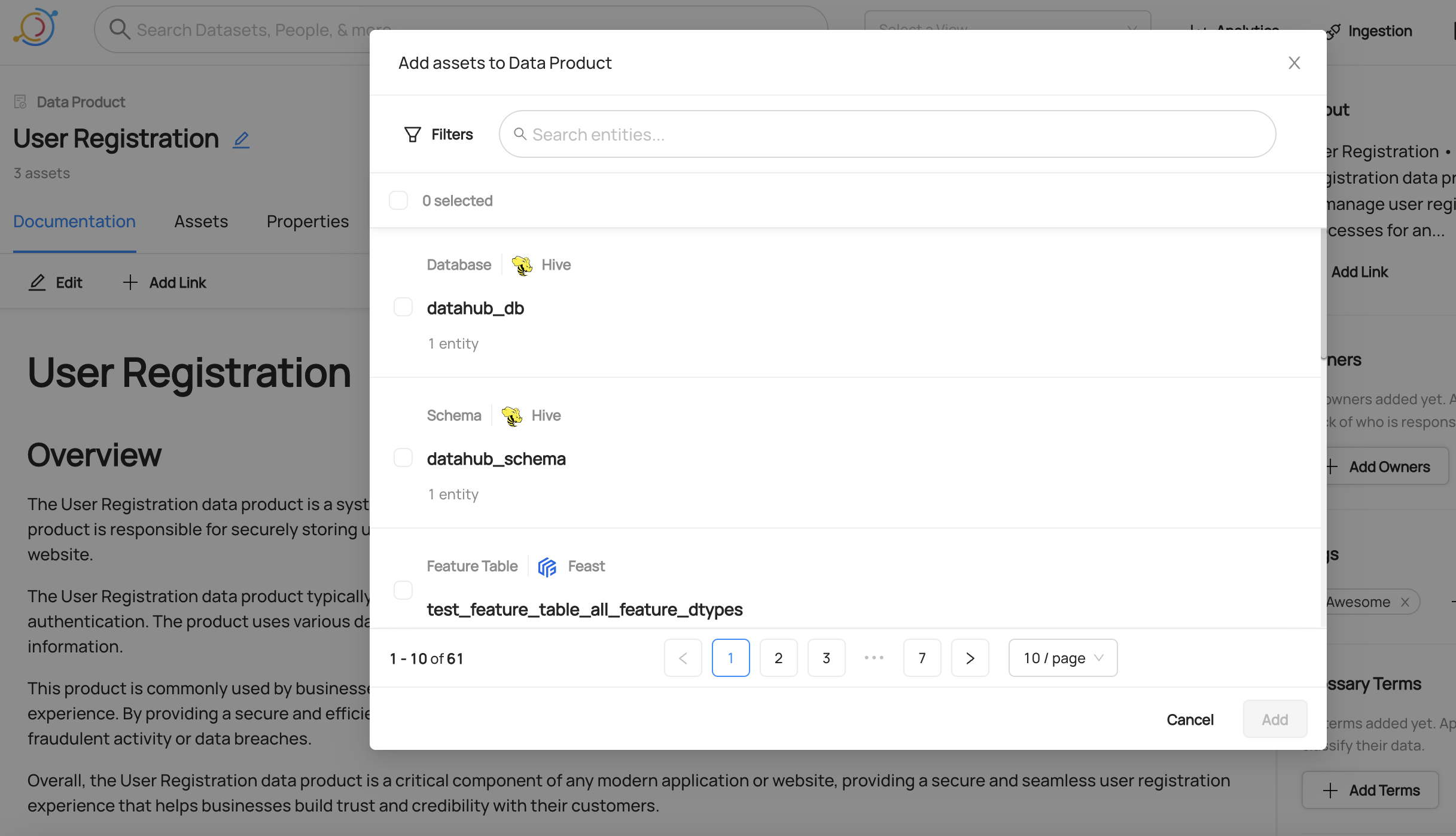
You can assign an asset to a Data Product either using the Data Product page as the starting point or the Asset's page as the starting point. On a Data Product page, click the 'Add Assets' button on the top right corner to add assets to the Data Product.
On an Asset's profile page, use the right sidebar to locate the Data Product section. Click 'Set Data Product', and then search for the Data Product you'd like to add this asset to. When you're done, click 'Add'.
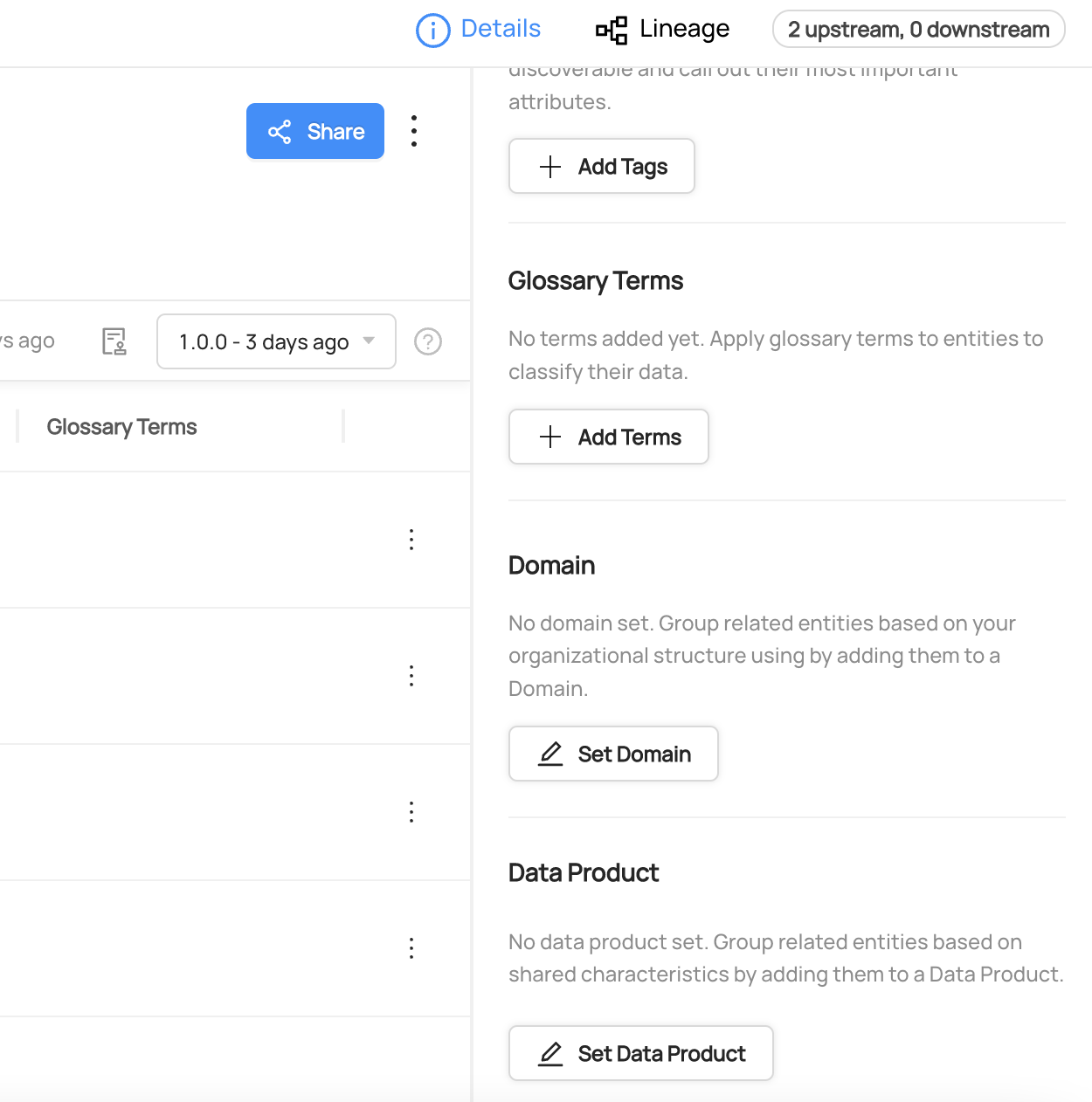
To remove an asset from a Data Product, click the 'x' icon on the Data Product label.
Notice: Adding or removing an asset from a Data Product requires the
Edit Data ProductMetadata Privilege, which can be granted by a Policy.
Creating a Data Product (YAML + git)
DataHub ships with a YAML-based Data Product spec for defining and managing Data Products as code.
Here is an example of a Data Product named "Pet of the Week" which belongs to the Marketing domain and contains three data assets. The Spec tab describes the JSON Schema spec for a DataHub data product file.
- Example
- Spec
# Inlined from /metadata-ingestion/examples/data_product/dataproduct.yaml
id: pet_of_the_week
domain: Marketing
display_name: Pet of the Week Campaign
description: |-
This campaign includes Pet of the Week data.
# List of assets that belong to this Data Product
assets:
- urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:snowflake,long_tail_companions.analytics.pet_details,PROD)
- urn:li:dashboard:(looker,dashboards.19)
- urn:li:dataFlow:(airflow,snowflake_load,prod)
owners:
- id: urn:li:corpuser:jdoe
type: BUSINESS_OWNER
# Tags associated with this Data Product
tags:
- urn:li:tag:adoption
# Glossary Terms associated with this Data Product
terms:
- urn:li:glossaryTerm:ClientsAndAccounts.AccountBalance
# Custom Properties
properties:
lifecycle: production
sla: 7am every day
When bare domain names like Marketing is used, datahub will first check if a domain like urn:li:domain:Marketing is provisioned, failing that; it will check for a provisioned domain that has the same name. If we are unable to resolve bare domain names to provisioned domains, then yaml-based ingestion will refuse to proceeed until the domain is provisioned on DataHub.
You can also provide fully-qualified domain names (e.g. urn:li:domain:dcadded3-2b70-4679-8b28-02ac9abc92eb) to ensure that no ingestion-time domain resolution is needed.
{
"title": "DataProduct",
"description": "This is a DataProduct class which represents a DataProduct\n\nArgs:\n id (str): The id of the Data Product\n domain (str): The domain that the Data Product belongs to. Either as a name or a fully-qualified urn.\n owners (Optional[List[str, Ownership]]): A list of owners and their types.\n display_name (Optional[str]): The name of the Data Product to display in the UI\n description (Optional[str]): A documentation string for the Data Product\n tags (Optional[List[str]]): An array of tags (either bare ids or urns) for the Data Product\n terms (Optional[List[str]]): An array of terms (either bare ids or urns) for the Data Product\n assets (List[str]): An array of entity urns that are part of the Data Product",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"title": "Id",
"type": "string"
},
"domain": {
"title": "Domain",
"type": "string"
},
"assets": {
"title": "Assets",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"display_name": {
"title": "Display Name",
"type": "string"
},
"owners": {
"title": "Owners",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string"
},
{
"$ref": "#/definitions/Ownership"
}
]
}
},
"description": {
"title": "Description",
"type": "string"
},
"tags": {
"title": "Tags",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"terms": {
"title": "Terms",
"type": "array",
"items": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"properties": {
"title": "Properties",
"type": "object",
"additionalProperties": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"external_url": {
"title": "External Url",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"id",
"domain"
],
"additionalProperties": false,
"definitions": {
"Ownership": {
"title": "Ownership",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"id": {
"title": "Id",
"type": "string"
},
"type": {
"title": "Type",
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"id",
"type"
],
"additionalProperties": false
}
}
}
To sync this yaml file to DataHub, use the datahub cli via the dataproduct group of commands.
datahub dataproduct upsert -f user_dataproduct.yaml
Keeping the YAML file sync-ed with changes in UI
The datahub cli allows you to keep this YAML file synced with changes happening in the UI. All you have to do is run the datahub dataproduct diff command.
Here is an example invocation that checks if there is any diff and updates the file in place:
datahub dataproduct diff -f user_dataproduct.yaml --update
This allows you to manage your data product definition in git while still allowing for edits in the UI. Business Users and Developers can both collaborate on the definition of a data product with ease using this workflow.
Advanced cli commands for managing Data Products
There are many more advanced cli commands for managing Data Products as code. Take a look at the Data Products section on the CLI reference guide for more details.
What updates are planned for the Data Products feature?
The following features are next on the roadmap for Data Products
- Support for marking data assets in a Data Product as private versus shareable for other teams to consume
- Support for declaring data lineage manually to upstream and downstream data products
- Support for declaring logical schema for Data Products
- Support for associating data contracts with Data Products
- Support for semantic versioning of the Data Product entity
Related Features
Need more help? Join the conversation in Slack!
